東京大学 羽藤研究グループ > 講座 > 2017 > 行動モデル夏の学校2017 > 当日のまとめ

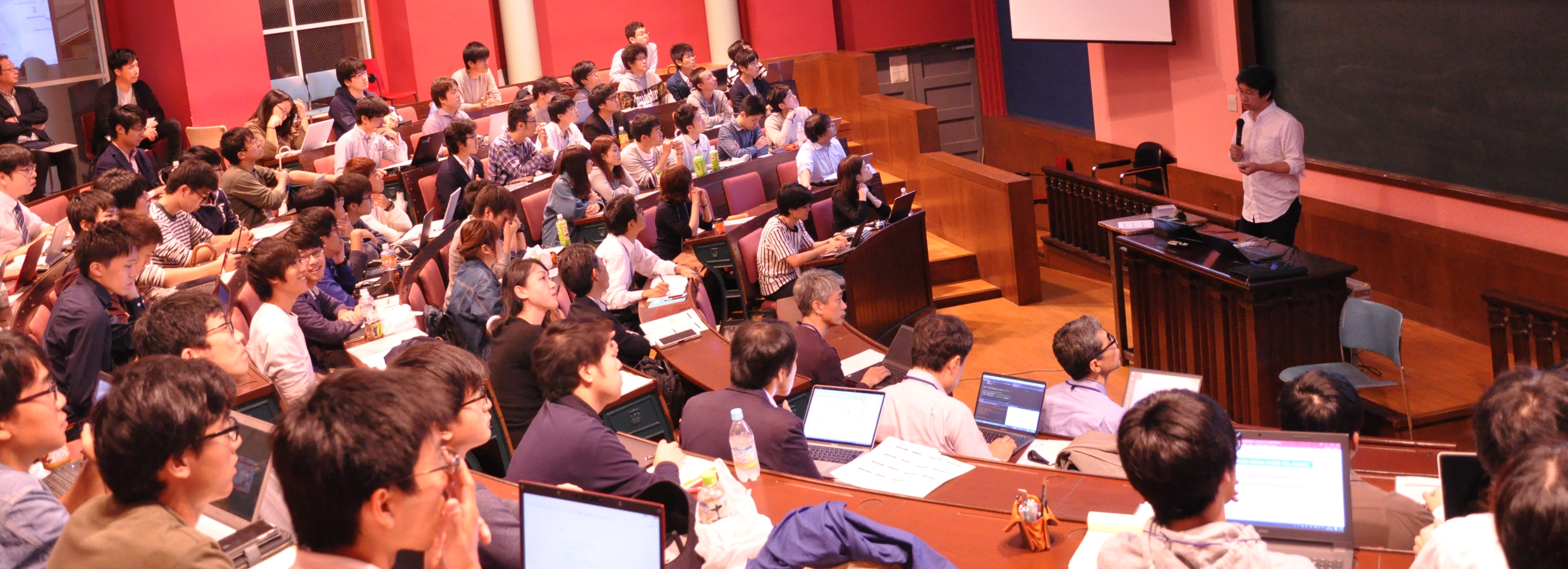
第16回行動モデル夏の学校2017は,東京都・文京区の東京大学本郷キャンパスにて,2017年10月13日から15日にかけての3日間,講師20名(うちResearch Workshop講演者6名),参加者87名(うち聴講者8名)によって行われました. 基調講演 Keynote lecture / 講義 Lectures / |
基調講演 Keynote Speech
Prof. Michel Bierlaire ( Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne )
Behavior Models and Optimization
|
行動モデルと最適化を援用したスマートモビリティについて,コンセプトからモデルフレーム,ケーススタディまでご講演頂いた.スマートモビリティ時代に重要なアジェンダとして,スマートフォンアプリを利用したデータ収集,行動モデルを利用した個々人への対応,最適化によるモビリティ供給の効率化,それらを統合したスマートプランニングが挙げられた.その上で具体的に,GPSなどスマートフォン端末のセンサーから生データを得た後,機械学習によるデータ分析と利用者に操作しやすいインターフェースによるデータの修正・追加をインタラクティブに行える観測システムであるFMS,サービスレベルを利用者に応じて変化させることでリアルタイムに車両を最適に配分するFMOD・AMOD,リアルタイムな交通状況等を予測するシミュレーションベースのシステム最適化とアプリに統合された情報とインセンティブによる個別メニュー最適化によって個人の経路選択を変えるMeMOT等について説明がなされた.(PDF Document) |

|
講義 Lectures
|
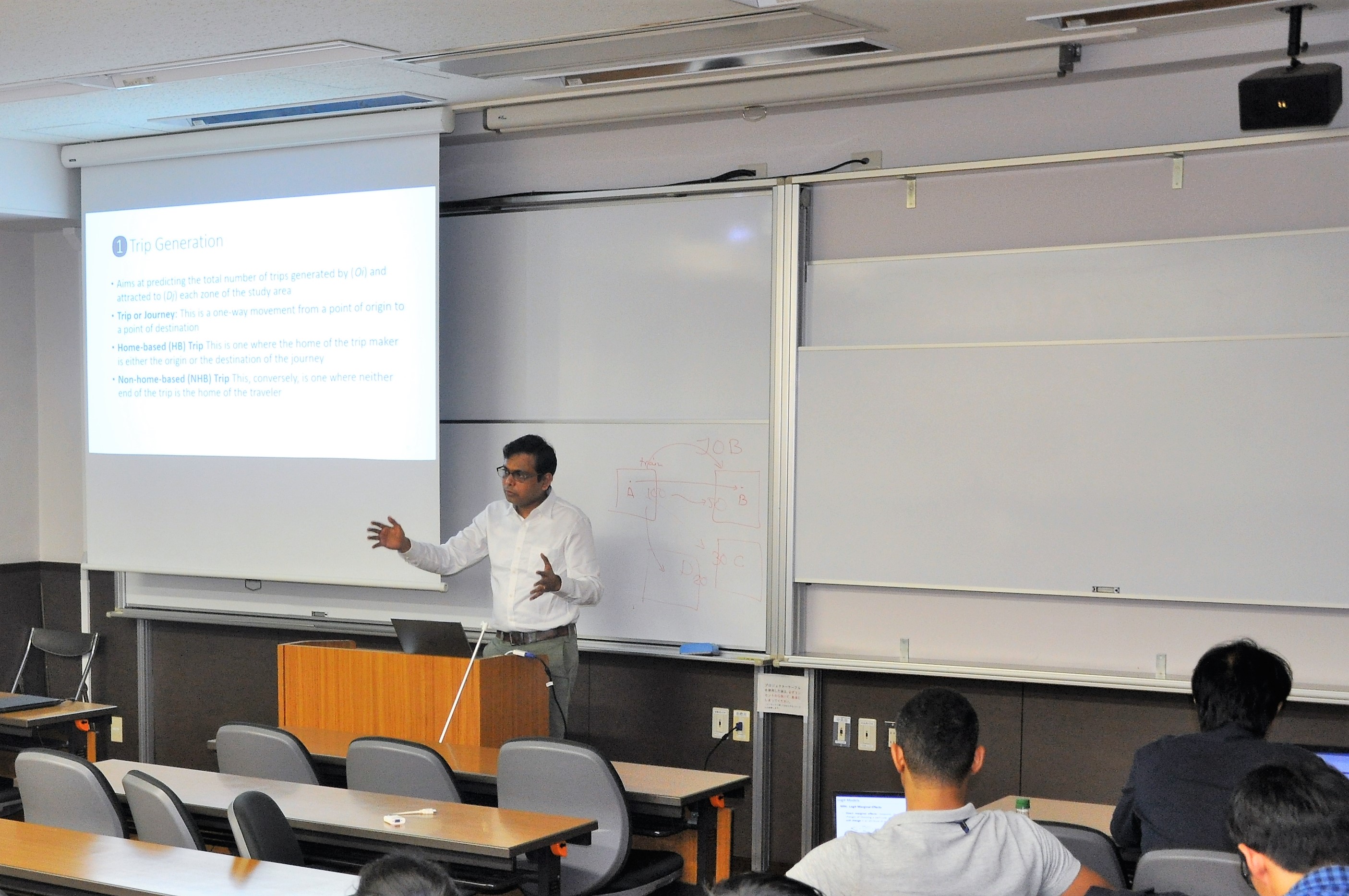
Arnab Jana(IIT Mumbai) The contents of this presentation is 1.Four-step modeling, 2.Choice Models, and 3.activity based modeling approach. Four-step modeling is by each model (gravity model in distribution step, etc.). To improve the travel demand estimation, choice model based on the random utility theory is used. Activity based modeling is focusing on the sequence of behavior in time-space matrix, and the better understanding and prediction of travel behavior. |

|
|
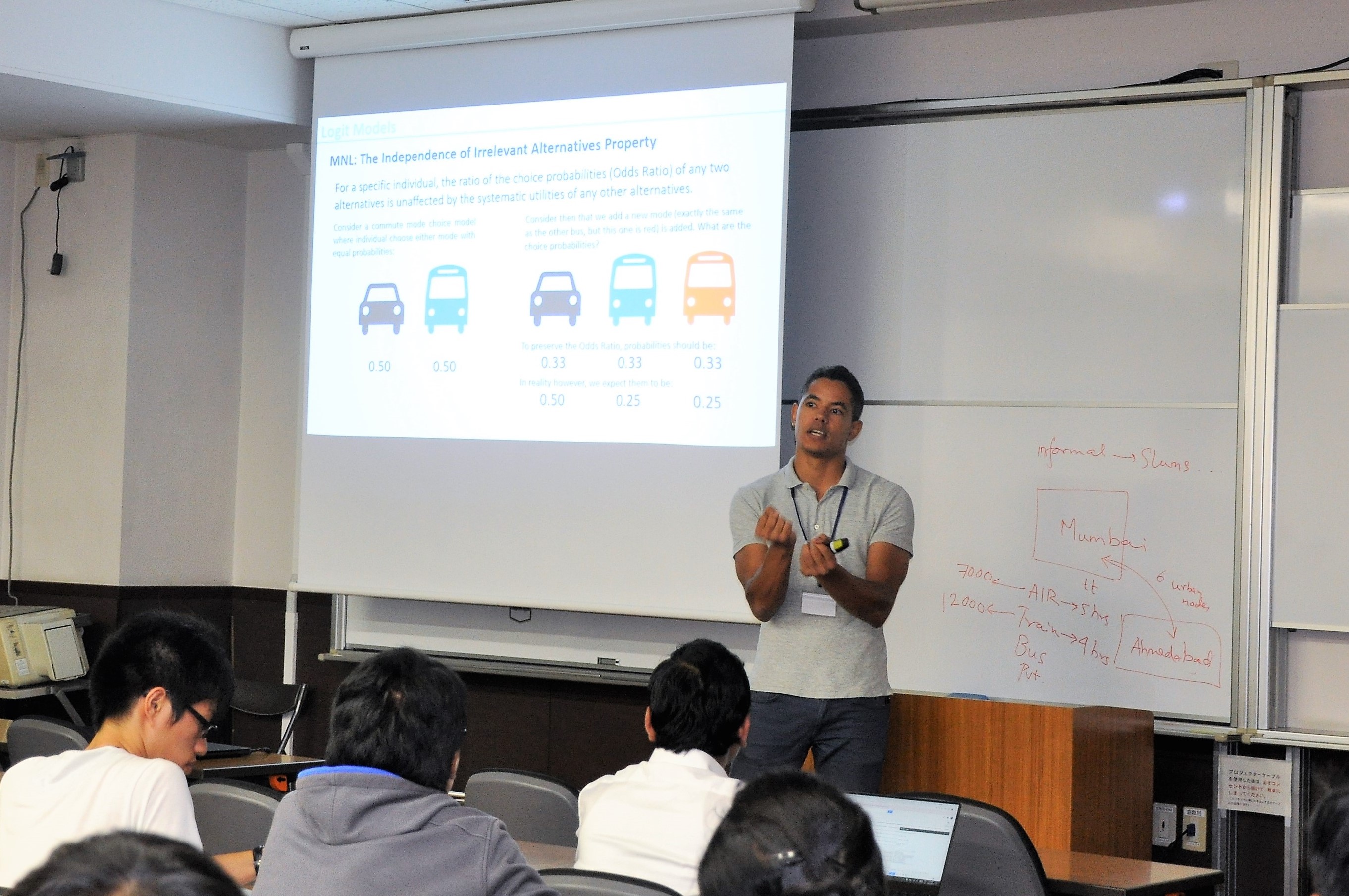
Giancarlos Troncoso Parady(Univ. Tokyo) 交通需要予測への新たなアプローチであるActivity-based modelingの導入を行う.離散選択モデルの基礎について,意思決定主体,選択肢,説明変数,意思決定ルールを定義し,誤差項の確率分布を仮定することで選択確率が計算できる.仮定する分布によって,Probit ModelやLogit Modelが定義される.さらに,Logit Modelにおけるスケースパラメータμの機能を説明した後,MNL modelが持つIIA特性についても赤バス青バス問題を例に説明がなされた.離散選択モデルは個人の交通行動を予測する一方で,政策分析では集計的な行動の評価が必要となる.需要変化の評価としては弾性値(elasticity)が代表的に用いられる.また,最尤推定法において用いられるアルゴリズムについても紹介がなされた. |

|
|
Makoto Chikaraishi(HiroshimaUniv.) 選択肢相関や分散の不均一性,選択肢集合の列挙等の問題を解決するために様々な発展的行動モデルが提案されてきた.中でもクローズドフォームのモデルは,McFadden(1978)によるG関数から導出でき,計算性が高い.誤差分布を特定せずに選択肢間の相関構造を記述できることも特徴の一つである.一方でMEVモデルにしか適用できないという制約があったが,Mattson et al.(2014)はMEVからGEV(一般化極値分布)へと拡張した一般化G関数を提案した.また経路列挙問題に対してはFosgerau(2013)に見られるような,選択肢を明示的に列挙せずにリンクごとの選択問題とみなすモデルが有効である. (PDF Document) |

|
|
Hideki Yaginuma(Tokyo Univ. of Science) オープンフォームのモデル選択肢間の誤差相関や分散不均一性を柔軟に表現することができる点で優れている.一方で多重積分の計算による計算コストの高さが根源的課題である.18号答申の需要予測の際には,東京の鉄道ネットワークの経路重複が大きな課題であったが,ODペアごとの共分散行列の各値を経路重複割合等で外生的に与える構造化プロビットモデルを用いて,精度向上に貢献した.一方でMixed logit modelは誤差項に2種類の分布を仮定するモデルで,そのパラメータの設定次第で他のGEVモデルを表現できるという特性を持ち,より柔軟なモデルとなっている.さらに,大雨・洪水を例に災害時の行動をETCデータを用いて分析し,センシングデータの活用についても紹介がなされた. (PDF Document) |

|
|
倉内慎也(愛媛大学) Profit Modelのようなopen-formのモデルに対して,MNLモデル(Multinomial Logic Model)はclosed-formであるというメリットを持つが,赤バス青バス問題に代表されるように,IIA特性が非現実的な結果をもたらすことがある.そこで誤差項間の相関を考慮できるNLモデル(Nested Logit Model)を適用することが考えられる.一方,MMNLモデル(Mixed Logit Model)では誤差項を分離することで,ロジットモデルの操作性を保ちつつ,より柔軟な誤差項相関を表現することを可能にする.選択確率はopen-formで記述されるため,推定にはシミュレーション法を用いる. (PDF Document) |

|
|
佐々木邦明(山梨大学) 行動モデルのパラメータ推定には一般的に最尤推定法を用い,最大化アルゴリズムを用いた繰り返し計算によって推定量を算出する.また誤差項を多変量正規分布で記述する場合はオープンフォームの積分計算が必要になるため,シミュレーションによる尤度計算を行う.またベイズ推定や効率的なサンプリングによるMCMC法による推定といった手法も存在する.各推定法にメリットデメリットが存在するため,選定するモデルに適した推定法を選択する必要がある.また政策シミュレーションを考える上では,意思決定の構造などのストーリを考慮した変数の設定,すなわち行動原理を熟慮した上でのモデルの構築が重要である. (PDF Document) |

|
|
山本俊行(名古屋大学) 客観的なサービス水準や社会経済属性だけでは離散選択行動を十分に表現できない場合の手法として,従来は非観測(latent)だった変数を離散選択モデルに導入したICLV(integrated choice and latent variable)モデルが紹介された.ICLVモデルには内生性バイアスの問題や将来予測が困難といった問題があるが,因果関係等の構造関係を同定でき,観測誤差等のバイアスを補正できるといった点において有用性が高い.また,社会心理学等の分野で変数間の関係を把握するために用いられている媒介変数(mediator)・調整変数(modetator)について導入があり,実際に媒介変数を用いた最新の研究が紹介された. (PDF Document) |

|
|
井料隆雅(神戸大学) 均衡という規範は,安定な均衡状態が一意に存在するときに限って信頼できる将来予測として利用できる.しかしながら,動的利用者均衡配分(DUE)モデルは基本的にWardropの第1原理から均衡状態を定義し,経路選択と出発時刻選択を内生化するモデルであるが,その均衡解は一意とは限らず,安定とも限らない.解の安定性の解析を進めるためには,人々が日々どのように行動を調整するのかを数理モデルに組み込む必要があるが,普遍的な規範を設定することが難しい.人々の日々の行動について,情報収集行動に着目して出発時刻選択モデルの数値計算を行うと,人々の情報の入手量によって均衡からの乖離度合いが異なる様子が確認できる.そこで均衡に収束しないことを前提とすれば,数学的に厳密に定義されているマルコフ連鎖の定常状態による記述が可能である. (PDF Document) |

|
Behavior in Networks Research Workshop
Research Presentation #1
|
Samal Sanjeewa Darmarathna (The University of Tokyo) Travel behavior is changed under uncertainty. Especially, we focus on extreme weather events and research the route choice behavior during them in β-Scaled recursive logit model framework.Checking the data in Tokyo, we realize that travel time parameter increases indicating difficulty to assess difference of travel time in links during heavy rainy day, that sequential discount rate β decreases indicating tendency towards the myopic decision making behaviour, and so on. |

|
Behavior and Network Optimaization Session
|
Keiichiro Hayakawa (TOYOTA CENTRAL R&D LABS., INC.) We establish fundamental algorithm to realize MaaS(Mobility as a Service) which allocate traffic resources optimally to users, considering heterogeneous users and slow traffic using auction-based approach. We have some problems to express this, but we introduce activity-state network which is an extended time-space network and time-constraint, and formalize activity-chain auction based on VCG mechanism. Moreover, We propose an algorithm, which is based on graph theory, to mitigate the computational complexity. Simulating based on this model, it can be said that by considering slow traffic, especially for cruising agents, the total social welfare can be increased. |

|
|
Qian Ge (Tokyo Institute of Technology) In Dynamic Traffic Assignment (DTA), we have to deal with Dynamic User Equilibrium(DUE), which is the assumption that the travel time of travels on all used paths is equal at user equilibrium in order to evaluate path cost. Firstly, variational inequalities formulation is adopted for DUE. However, this approach imposes high computation burden. Therefore, surrogate modeling is adopted to develop a DTA solver considering macroscopic traffic dynamics. It describes the mapping from path flow to path cost and can be viewed as a local approximation of mapping for the solution point. It performs better when the distance between sampled data and the solution are small. By iteratively solving the DUE problem, the accuracy of surrogate model will be improved accordingly. |

|
|
Takao Dantsuji (Tokyo Institute of Technology) Transportation demand management (TDM) has problems that we cannot solve easily; congestion. Dedicated bus lane is regarded as one of the most promising solutions. In this study, road space allocation of the dedicated bus lanes is optimized quantitatively by using 3D-MFD (Macroscopic fundamental diagram). This approach adopts both static optimization model and simulation analysis model. In the Geneva case, around 15% of the space to the bus lanes is the most efficient. In the future study, it is useful to investigate the universality of this approach further with the Tokyo case, by improving the aggregate logit model or calibrating by the detectors data. |
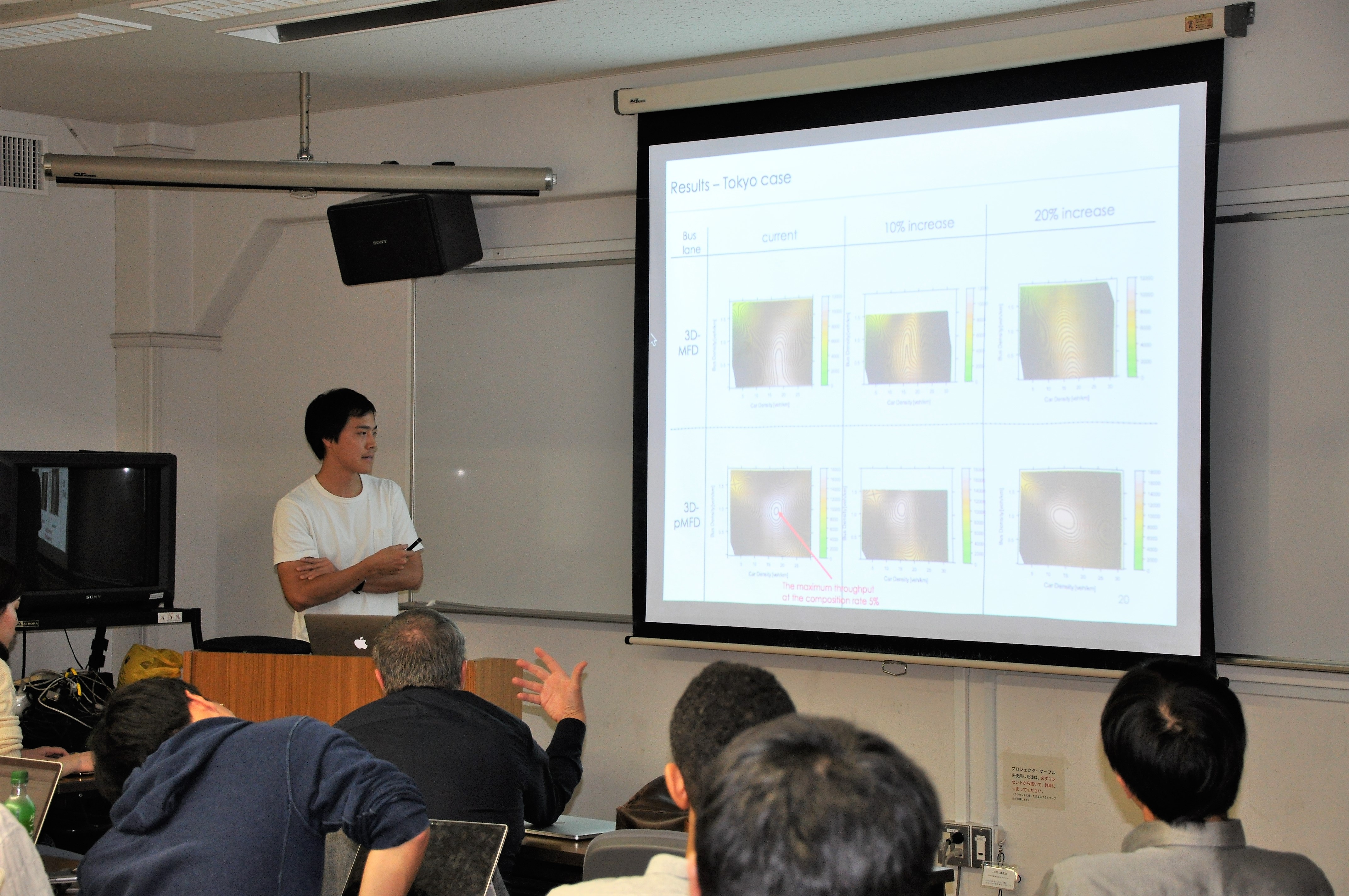

|
Special Research Talk
|
Prof. Michel Bierlaire (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne) Special Reserach Talkでは,EPFL(ローザンヌ工科大学)で現在進行中の研究プロジェクトが紹介された.ガーナでの交通システムの分析を始め,EUでの歩行者流動分析,自動運転実現に向けた歩行者検出技術,スイス国鉄のダイヤ最適化などの多岐にわたる研究プロジェクトが紹介されたあと,"World without Car"の実現を目指して,動く歩道を都市に張り巡らせるという壮大なプロジェクトの提示によって紹介を締めくくった.最後に,若い研究者に向けて,日々進化する方法論と現実世界で起こっている問題の両方に注意を払い,マッチさせ続けていく努力が必要であるというメッセージが送られた. |
|
Research Presentation #2
|
Karan Barpete (IIT Mumbai)
|

|
|
Ryuichi Shibasaki (The University of Tokyo)
|
|
演習 Group work
課題:プローブパーソンデータを用いた行動モデル推定
プローブパーソンデータ(ロケーションデータ,ウェブダイアリー)・土地利用データ・交通ネットワークデータを用いて,離散選択モデルをはじめとした行動モデルの構築と推定を,4~7人での班ごとに行い,成果を発表しました.

|
team A (IIT Bombay) pdf / code Abstract: MXL and MNL mode choice model in Yokohama city 1. The interaction with age 2. Mode choice behavior during peak hours
|

|
team B(Nagoya Univ.(English)) pdf / code Abstract: Travel behavior model has been a powerful tool for transportation programs and policy implications since early day. In association to the quick changing of socio-demographic situation in Japan; our team came up with an idea to investigate on mode choice preferences between motorized and non-motorized by using MNL and NL estimation model. The data was conducted in 2009 targeted Japanese’s people living in Yokohama city, the second largest city in Japan by population. The result shows that the elder people are less likely to trip with bicycle. And during peak hour, bike is not expected to be used, while train is highly preferable.
|
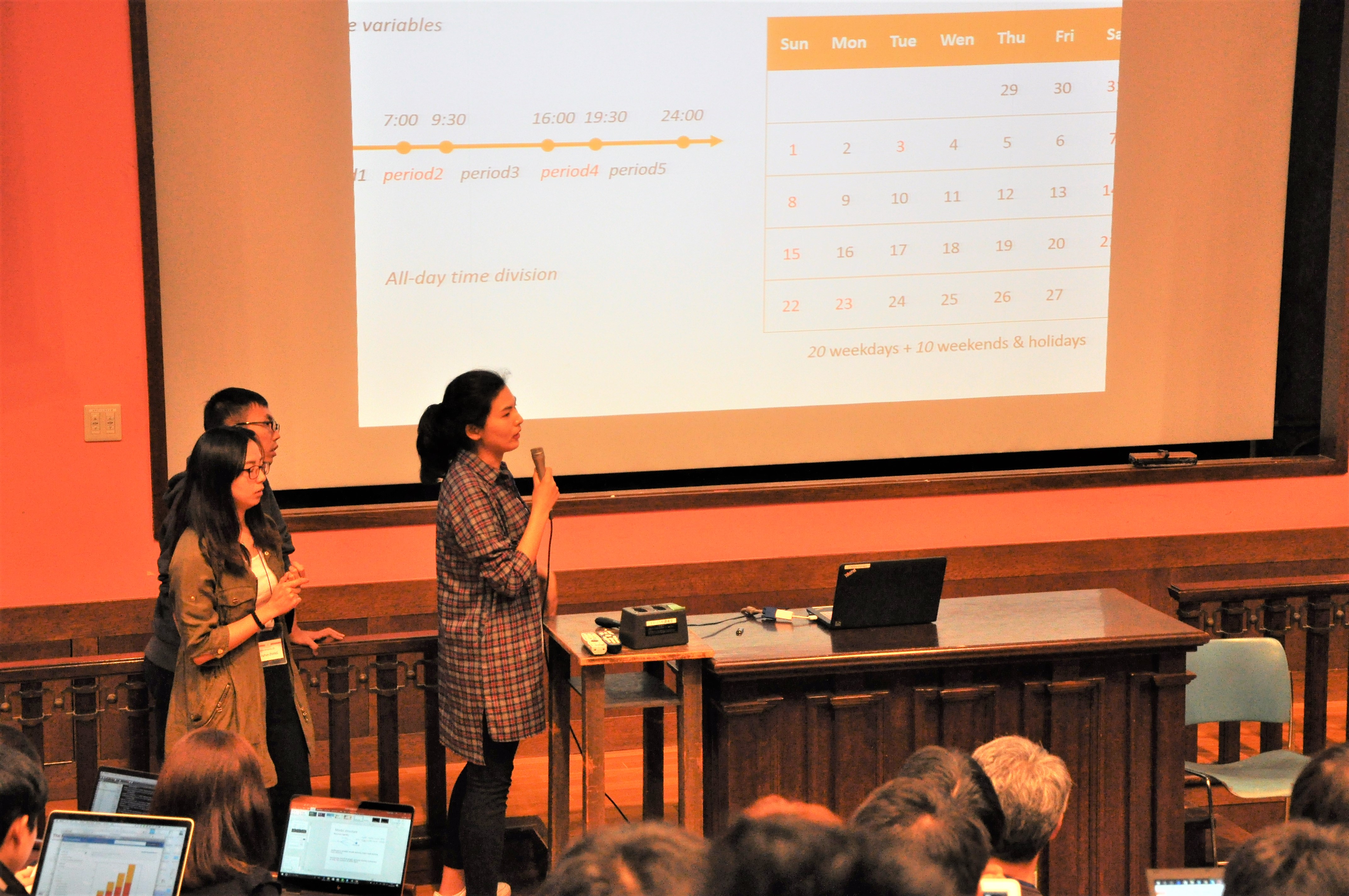

|
team C(Hiroshima Univ.(English)) pdf / code Abstract: Team C from Hiroshima Univ estimated the NL model for the relationship between departure time and travel mode choice.
|

|
発表概要:短距離トリップでの自動車利用量削減を目的とした特定トリップへの課金政策及び公共交通機関運賃値下げ政策の感度分析を目指し、mnlによる交通機関選択モデルの構築を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:MNLモデルにより交通手段選択モデルを構築しました。政策シミュレーションではロードプライシングの交通手段選択に及ぼす影響の分析を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:NL型で交通手段選択モデルを用いて、完全自動運転化による影響を分析しました。年齢を加味するなど変数を工夫し、推定では0.663という高い尤度比を導くことに成功しました。
|

|
発表概要:自転車の経路選択の逐次性に着目し、RLモデルによる推定を行いました。スパースなネットワークデータを作成し、計算量を削減して計算を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:"ぼっち"、つまり単独行動する人の行動特性を考慮し、その上で、単独行動者にとって魅力的な空間が持つ特性を検討しました。
|
|
発表概要:ビッグデータ活用に向けても有用と考えられる、新個人属性推定に挑戦しました。機械学習により各個人属性の目的の推定を行い、クラスタ分析を用いた新個人属性の有用性を示しました。
|

|
発表概要:終業後の回遊行動に着目し、行動選択モデルを構築しました。政策シミュレーションでは、プレミアムフライデーや商業施設面積の増大が回遊率に与える影響を分析しました。
|

|
team K(Kyoto Univ.) pdf / code Abstract: Team K evaluated the current equity level of the public transport in Yokohama city and predicted the future one after changing the fare structure from the perspective of users’ generalized cost via real data (pp data of Yokohama City). Gini coefficient is introduced to quantify the equity of public transport and MNL is used for the calibration of utility function as well as the estimation on changes in mode choice.
|

|
発表概要:イグレス時間とアグレス時間を考慮したCNLによる交通手段選択モデルを構築しました。さらにネットワークデータをクリーニングし、"交通量配分"による政策評価を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:行動の合理性を独自に定義し、合理的行動と非合理的行動の二項ロジットモデルを構築しました。さらに、交通手段選択に関して多項ロジットモデルを用いて推定を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:平日の行動に着目した休日の余暇活動の都市間比較分析と題し、外部財を加えたMDCEVモデルを用いて推定を行いました。
|

|
発表概要:横浜の歩行者に対する政策に注目して、ロードプライシングによる利益を財源として歩行の促進を図るような政策の評価を目指し、MXLモデルなどによる推定に挑戦しました。
|

|
発表概要:プレミアムフライデーの効果分析を目指しました。私事活動有無の逐次的な二項ロジットモデルの推定では、前日の活動が活動有無に与える影響なども示しました。
|
表彰 Award
行動モデル夏の学校には例年,数理的にモデリングをつめられていたグループには,故・上田孝行先生にちなんだ香住賞が,行動分析によって興味深いfact findingを実現したグループには,故・北村隆一先生にちなんだDavis賞が,モデルの精度指標の一つである尤度比が最も高かったグループには,尤度比賞が送られます.今年度の受賞チームは以下の通りです.
香住賞 :Nチーム(熊本大学)
Davis賞:Iチーム(山梨大学)
尤度比賞:Fチーム(東京理科大学)
1位:Lチーム(神戸大学)、Nチーム(熊本大学) 3位:Iチーム(山梨大学)

